
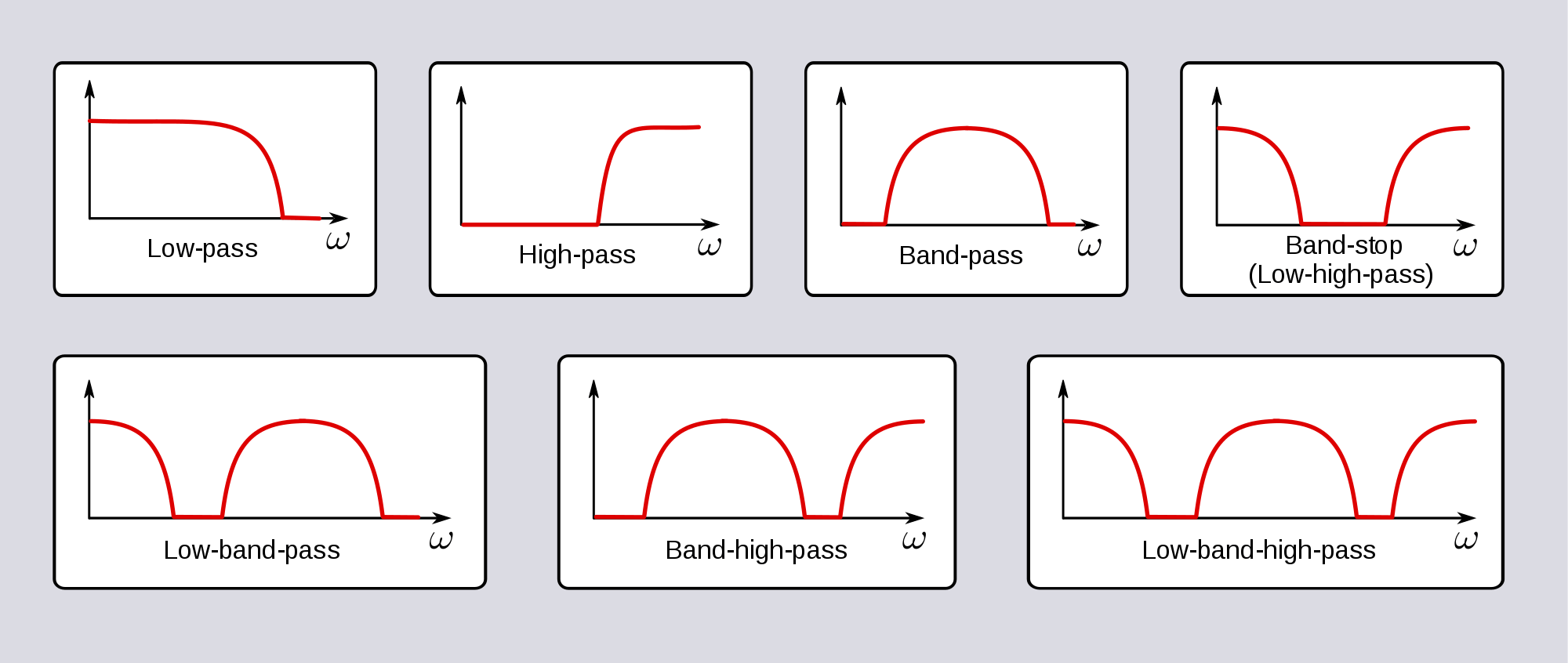
 Comb Filter – This eliminates frequencies not found within a series of chosen frequency notches. Notch / Band Reject – This response curve eliminates only frequencies that are within a specified band. Band Pass – This response curve eliminates all frequencies that are NOT within a specified frequency band. High Pass – This response curve eliminates all frequencies below a specified frequency, allowing high frequencies to “pass”.
Comb Filter – This eliminates frequencies not found within a series of chosen frequency notches. Notch / Band Reject – This response curve eliminates only frequencies that are within a specified band. Band Pass – This response curve eliminates all frequencies that are NOT within a specified frequency band. High Pass – This response curve eliminates all frequencies below a specified frequency, allowing high frequencies to “pass”.  Low Pass – This response curve eliminates all frequencies above a specified frequency, allowing low frequencies to “pass”. There are an almost infinite amount of possible response curves that a filter can have, and the most common types used in synths are: To put it simply, a filter gets rid of some frequencies within a soundwave, alters the harmonic content of a signal, which results in a change of timbre. From indie, to hardcore EDM, to lofi hip hop, filters are used to shape the sonic output and emotive quality of sounds within a track. To simulate this, simply change the Cutoff Frequency when opening the door.“What are the best free filter VST plugins out there in 2021?”įilters are an incredibly useful technique to manipulate and automate the timbre of a sound, and this production method is found in a huge, diverse range of genres. The high frequencies of a sound being emitted from behind a door will be filtered out by the door and so won’t reach the listener. For example, to compliment a visual fog effect add a subtle low-pass to the Audio Listener A component that acts like a microphone, receiving sound from Audio Sources in the scene and outputting to the computer speakers.
Low Pass – This response curve eliminates all frequencies above a specified frequency, allowing low frequencies to “pass”. There are an almost infinite amount of possible response curves that a filter can have, and the most common types used in synths are: To put it simply, a filter gets rid of some frequencies within a soundwave, alters the harmonic content of a signal, which results in a change of timbre. From indie, to hardcore EDM, to lofi hip hop, filters are used to shape the sonic output and emotive quality of sounds within a track. To simulate this, simply change the Cutoff Frequency when opening the door.“What are the best free filter VST plugins out there in 2021?”įilters are an incredibly useful technique to manipulate and automate the timbre of a sound, and this production method is found in a huge, diverse range of genres. The high frequencies of a sound being emitted from behind a door will be filtered out by the door and so won’t reach the listener. For example, to compliment a visual fog effect add a subtle low-pass to the Audio Listener A component that acts like a microphone, receiving sound from Audio Sources in the scene and outputting to the computer speakers. 
Low-Pass (shelving) filter Hi-Pass (shelving) filter Band pass filter. Sounds propagates very differently given the environment. Equalisers (EQ) are used to modify the amplitude of selected parts of the. The Audio Low Pass Filter has a Rolloff curve associated with it, making it possible to set Cutoff Frequency over distance between the AudioSource and the AudioListener.
Higher lowpass resonance quality indicates a lower rate of energy loss, that is the oscillations die out more slowly. The signal flow graph (or simulation diagram) for this little filter is given in Fig. The Lowpass Resonance Q (short for Lowpass Resonance Quality Factor) determines how much the filter’s self-resonance is dampened. The simplest (and by no means ideal) low-pass filter is given by the following difference equation : (2.1) where is the filter input amplitude at time (or sample), and is the output amplitude at time. Lowpass resonance quality value (range 1.0 to 10.0, default = 1.0). Lowpass cutoff frequency in Hertz (range 0.0 to 22000.0, default = 5000.0). The Audio Low Pass Filter passes low frequencies of an AudioSource or all sound reaching an AudioListener while removing frequencies higher than the Cutoff Frequency.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
